Contents
- History
- Ancient Trade Routes
- Modes of Transport
- Train and Rail Systems
- Overview of Bus Networks
- Autos & Shared Vehicles
- Air Travel
- Ferries & Water Transport
- Traffic Map
- Communication Networks
- Newspapers & Magazines
- Radio & Broadcasting
- What’s on the Billboards? A Look at Jalgaon’s Hoardings
- Graphs
- Road Safety and Violations
- A. Cases of Road Safety Violations
- B. Fines Collected from Road Safety Violations
- C. Vehicles involved in Road Accidents
- D. Age Groups of People Involved in Road Accidents
- E. Reported Road Accidents
- F. Type of Road Accidents
- G. Reported Injuries and Fatalities due to Road Accidents
- H. Injuries and Deaths by Type of Road
- I. Reported Road Accidents by Month
- J. Injuries and Deaths from Road Accidents (Time of Day)
- Transport Infrastructure
- A. Household Access to Transportation Assets
- B. Length of Roads
- C. Material of Roads
- Bus Transport
- A. Number of Buses
- B. Number of Bus Routes
- C. Length of Bus Routes
- D. Average Length of Bus Routes
- E. Daily Average Number of Passengers on Buses
- F. Revenue from Transportation
- G. Average Earnings per Passenger
- Communication and Media
- A. Household Access to Communication Assets
- B. Newspaper and Magazines Published
- C. Composition of Publication Frequencies
- Sources
JALGAON
Transport & Communication
Last updated on 6 November 2025. Help us improve the information on this page by clicking on suggest edits or writing to us.
History
Ancient Trade Routes
Jalgaon district lies in a region that once formed part of major inland trade routes connecting Gujarat, central India, and the Deccan. Long before modern roads and railways, traders carried cotton, grain, and textiles along rough tracks and mountain passes that crossed this area.
According to the Khandesh Gazetteer (1880), many key routes passed through towns like Amalner, Chopda, Parola, Erandol, Savda, Bhadgaon, and Pachora, linking them to bigger trade centres such as Burhanpur (Madhya Pradesh) and Surat (Gujarat). North-eastern routes led through the Dhaulibari Pass towards Malwa, while others connected south to Ajanta and Sambhaji Nagar. Feeder tracks connected local villages to the main Surat–Burhanpur–Agra trade route, which carried goods to Gujarat’s ports and on to northern India. These early routes helped local markets grow and shaped how people settled across what is Jalgaon district.
Modes of Transport
Train and Rail Systems
Jalgaon district is served by the Bhusawal Division of the Central Railway Zone, one of the busiest rail divisions in India. Bhusawal Division’s network is central to the district’s transport and economy and has linked Jalgaon’s cotton-growing areas to key markets across the country.
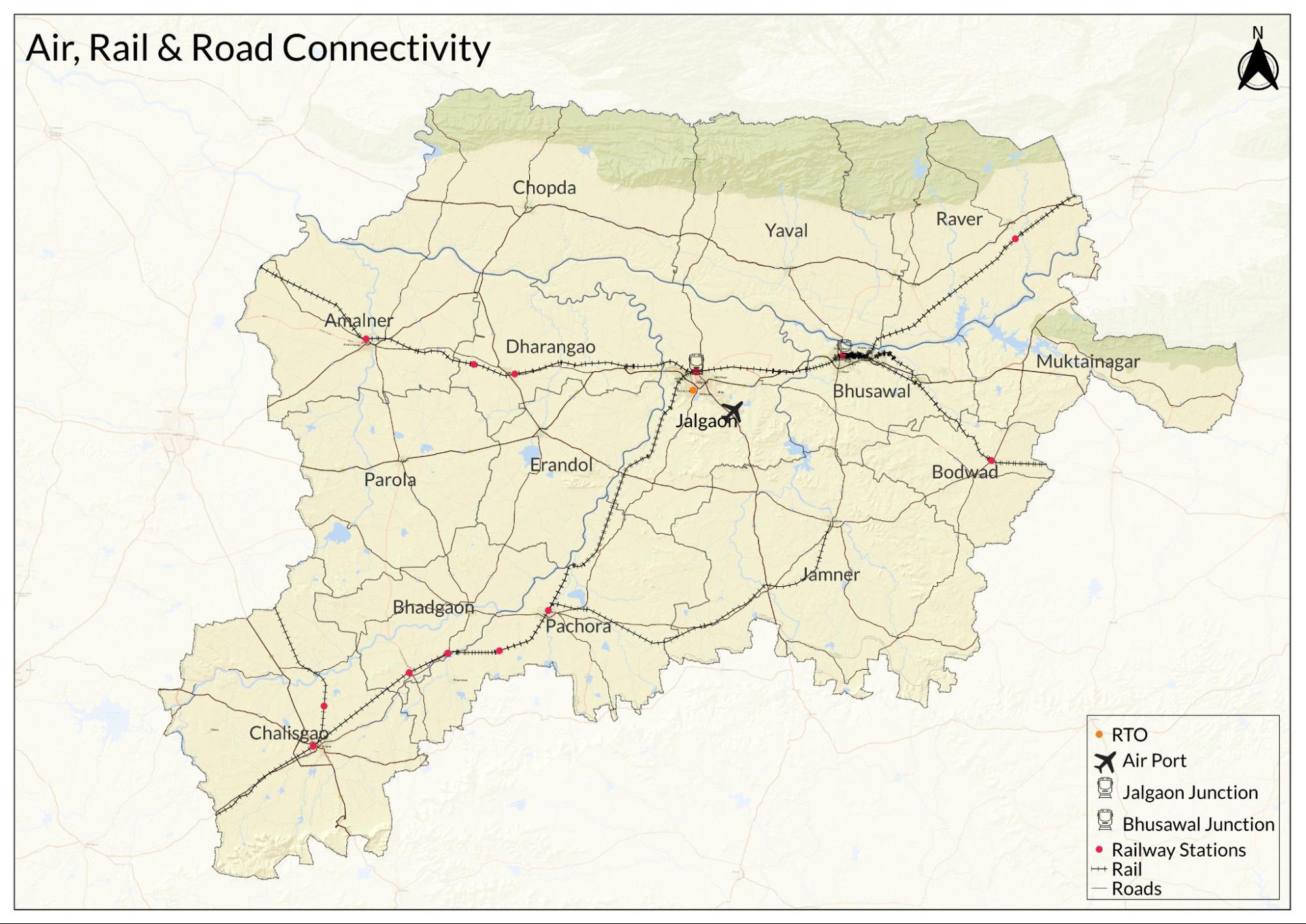
Railways first came to the region under the British, when the Great Indian Peninsula Railway (GIPR) was extended through Khandesh. Work began in 1852, and by 1865, about 229 km of track crossed what is now Jalgaon district. The line entered near Naydongri (Nashik district) and followed the Girna River, passing through major stations including Chalisgaon, Kajgaon, Pachora, Jalgaon, Bhadli, and Bhusawal.
Bhusawal became the main railway centre for the district. From here, the line branched towards Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh) and Nagpur, giving Jalgaon a direct rail link to central and eastern India. Bhusawal developed into a major railway junction and yard, which is still among the largest in Asia, with around 243 tracks, handling about 150 trains daily.

The railway helped Jalgaon become one of India’s leading cotton-growing and trading districts. The line connected farms to Mumbai’s port by 1863, speeding up the export of cotton and other produce.
During British rule, Bhusawal station was built with workshops, staff quarters, gardens, reading rooms, and a gymkhana for railway officials. It also housed one of Asia’s largest steam locomotive sheds, which was later converted for diesel engines in 1964 and electric engines in the 1950s, keeping the division modern and efficient.
Today, the Bhusawal Division remains vital for both freight and passengers. It connects Jalgaon’s towns with Mumbai, Nagpur, and other major cities. The Rail Museum at Bhusawal highlights this history with old locomotives, carriages, and railway equipment, marking how the rail network shaped Jalgaon’s development.
Overview of Bus Networks
Bus services remain a main mode of transport for travel between villages, towns, and nearby districts in Jalgaon. The Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation (MSRTC) operates most public buses, which locals often call “Laal Dabba” or “Laal Pari” because of their distinctive red colour. These buses connect remote areas to markets and railway stations, and continue to serve daily commuters and travellers where rail lines do not reach.
In 2023, it was announced that the Jalgaon Municipal Council had planned to start a dedicated city bus service to meet growing demand for urban transport within Jalgaon city. According to local reports, the new municipal buses will operate from the old bus stand, with land and route approvals provided by MSRTC. Once fully operational, these city buses will add an affordable option for daily commuting inside Jalgaon’s urban area.
Autos & Shared Vehicles
For local travel within towns and cities, auto rickshaws are widely used. A common option is the shared rickshaw, known locally as a “vadap”, which carries about six passengers along fixed routes. Shared autos are popular because they are more affordable than private hires and run frequently. Although most auto rickshaws have fare meters, they are rarely used in practice, so passengers usually agree on the fare in advance or pay a set shared rate.
Air Travel
Jalgaon district is served by Jalgaon Airport, which connects the region to other parts of India by air. Located in Jalgaon city, the airport first opened in 1973 to improve access for the surrounding districts in northern Maharashtra. After a brief suspension of services, commercial flights have resumed in recent years, linking Jalgaon with cities such as Pune, Hyderabad, and Goa.

Ferries & Water Transport
Water transport was likely used for local conveyance in Jalgaon district long before modern bridges and roads were built. Today, locals say that in rural parts of Jalgaon district, boats are still used where bridges are missing or where rivers are too wide to cross easily on foot. This is common along parts of the Tapi River, where small local boats help villagers reach markets, schools, and nearby settlements.
In addition to basic ferry use, Jalgaon has a few scenic spots where boating is a popular leisure activity. Hatnur Dam is well known for casual boating; it remains open year-round and does not charge an entry fee. Waghur Dam offers a similar quiet setting for visitors. The Mahatma Gandhi Garden in Jalgaon city also provides boating facilities, giving families and tourists a chance to enjoy the district’s green spaces.
A newer addition is the Backwoods Emerald Resort, which recently introduced houseboat services near Jalgaon. This has become an emerging draw for visitors looking for a different type of stay and experience on the water.

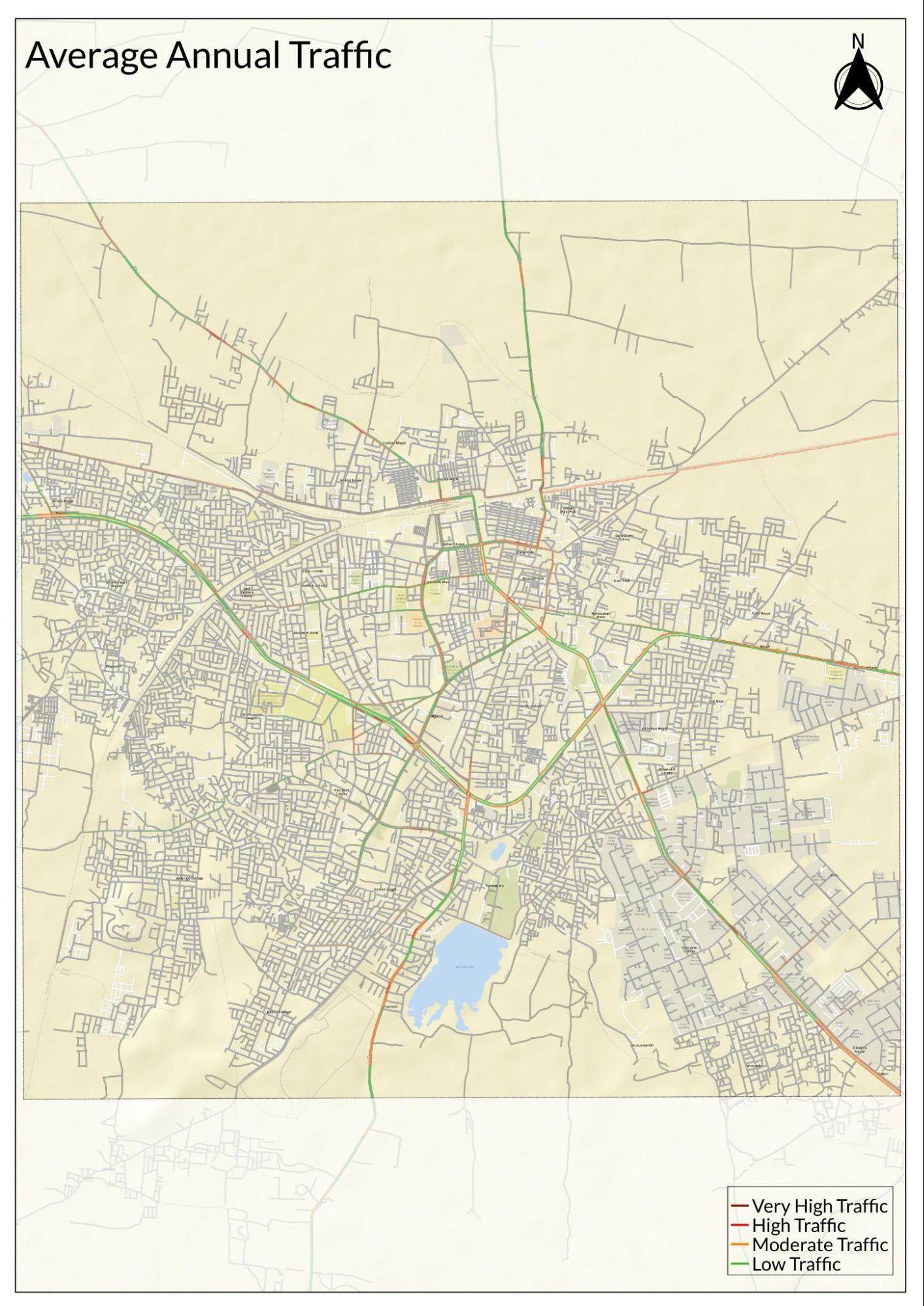
Traffic Map
Communication Networks
Newspapers & Magazines
In the 1880s, Jalgaon district was already home to local Marathi newspaper publishing. According to the Khandesh Gazetteer (1880), the Jalgaon Samachar (Jalgaon News) was published as a weekly Marathi newspaper in Jalgaon town at that time.
Today, Jalgaon district has a wide range of Marathi newspapers that remain popular for local and regional news. Leading Marathi publications include Lokmat, Sakal, Deshdoot, Pudhari, Jalgaon Tarun Bharat, and Divya Marathi. Alongside these, English newspapers such as The Times of India, The Indian Express, and Hindustan Times are also available, as well as Hindi dailies like Dainik Bhaskar, Dainik Jagran, and Amar Ujala.
Radio & Broadcasting
Alongside newspapers and magazines, community radio has become an important source of local information and outreach in Jalgaon district. Radio Manbhavan, operated by Moolji Jaitha College, began broadcasting on 90.8 FM on 14 April 2022. The station focuses on programs that give space to local voices, with special attention to reaching marginalised groups in the community.
Under the Rural Broadcasting Contributory Scheme, the Government of Maharashtra has supported the installation of radio sets in gram panchayat offices across rural areas. These broadcasts provide educational and cultural content, helping to share useful information and strengthen community ties, especially in villages with limited access to other media.
What’s on the Billboards? A Look at Jalgaon’s Hoardings
Hoardings in Jalgaon district mainly advertise local businesses, medical services, schools, and coaching classes. Because agriculture is such a big part of the area, locals say that ads for seeds, fertilisers, and farm tools are also common, especially near rural markets.
During elections, political banners and hoardings line busy roads and town centres, with party symbols and candidate posters placed for maximum visibility. Cultural events, fairs, and local gatherings are often advertised too.
Most hoardings are put up along highways, bus stands, crossroads, and market streets where they catch the most attention.

Graphs
Road Safety and Violations
Transport Infrastructure
Bus Transport
Communication and Media
Sources
E Rail. Bhusaval Railway Division Information.https://erail.in/info/central-railway-bhusav…
Gazetteer Department. 1880 (reprinted in 1985). Gazetteers of the Bombay Presidency: Khandesh District, Volume XII. Gazetteer Department, Government of Maharashtra, Mumbai.
IRCFA. Indian Railways History: 1900 - 1946.https://irfca.org/faq/faq-history3.html
Sakal. 2023.Jalgaon Municipality Bus: मनपाची शहर बससेवा जुन्या बसस्थानकापासून; एस. टी. महामंडळाची तत्त्वतः मान्यता. Sakal.https://www.esakal.com/jalgaon/municipal-cit…
The Times of India. 2023. Flights From Jalgaon to Pune, Goa, Hyderabad in Feb. Times of India.https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/nas…
World Health Organization.Road Safety. WHO, Geneva.https://www.who.int/health-topics/road-safet…
Last updated on 6 November 2025. Help us improve the information on this page by clicking on suggest edits or writing to us.