Contents
- History
- Modes of Transport
- Train and Rail Systems
- Overview of Bus Networks
- Ferries & Water Transport
- Traffic Map
- Communication Networks
- Newspapers & Magazines
- Graphs
- Road Safety and Violations
- A. Cases of Road Safety Violations
- B. Fines Collected from Road Safety Violations
- C. Vehicles involved in Road Accidents
- D. Age Groups of People Involved in Road Accidents
- E. Reported Road Accidents
- F. Type of Road Accidents
- G. Reported Injuries and Fatalities due to Road Accidents
- H. Injuries and Deaths by Type of Road
- I. Reported Road Accidents by Month
- J. Injuries and Deaths from Road Accidents (Time of Day)
- Transport Infrastructure
- A. Household Access to Transportation Assets
- B. Length of Roads
- C. Material of Roads
- Bus Transport
- A. Number of Buses
- B. Number of Bus Routes
- C. Length of Bus Routes
- D. Average Length of Bus Routes
- E. Daily Average Number of Passengers on Buses
- F. Revenue from Transportation
- G. Average Earnings per Passenger
- Communication and Media
- A. Household Access to Communication Assets
- B. Newspaper and Magazines Published
- C. Composition of Publication Frequencies
- Sources
PARBHANI
Transport & Communication
Last updated on 6 November 2025. Help us improve the information on this page by clicking on suggest edits or writing to us.
History
Parbhani is situated within the Marathwada region, which historically lay along routes connecting parts of the Deccan. Bina Sengar (2016) makes note of how broader trade networks in the Deccan during the 18th and 19th centuries linked regions such as Marathwada (where Parbhani lies), Khandesh, Vidarbha, Warangal, and Hyderabad through a combination of highways and paths that crossed the Vindhya and Satpura ranges. These routes enabled the movement of goods ranging from daily necessities to luxury items.
While little is known of Parbhani’s commercial prominence during this period, it likely benefited from its proximity to these larger trade corridors. Local communities in the area might have engaged with traders and markets connected to the wider Deccan networks.
Modes of Transport
Train and Rail Systems
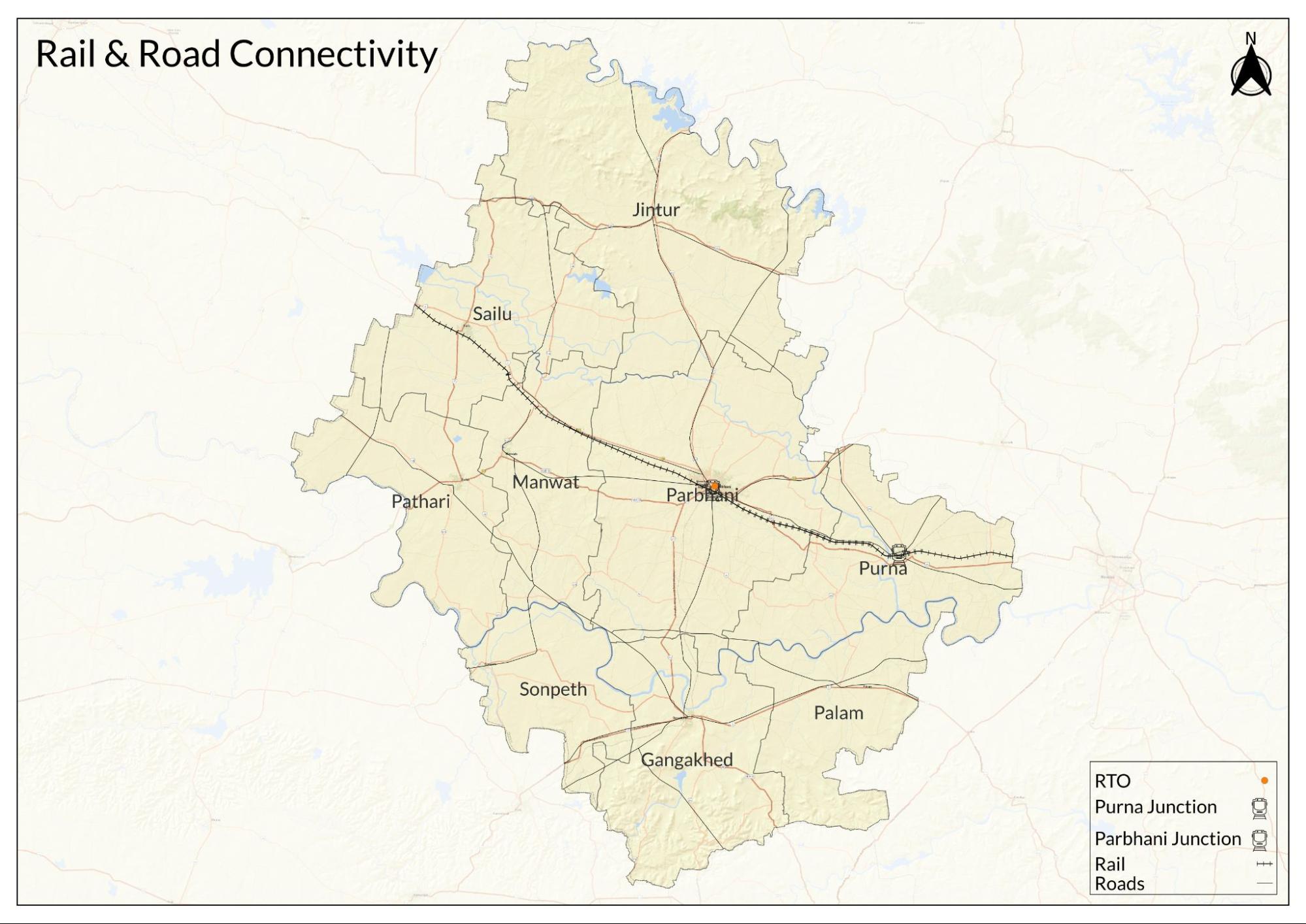
Parbhani district is part of the Nanded Railway Division under the South Central Railway zone. The main railway stations in the district are Parbhani Junction and Purna Junction, both of which serve as important stops for passenger and freight trains in the region.

The railway infrastructure in the district developed during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. The first major line to pass through the area was the Manmad–Kacheguda line, planned during the final years of the nineteenth century and opened in phases between 1899 and 1905. This line provided an important link between Secunderabad in present-day Telangana and Manmad in Nashik, Maharashtra, passing through Parbhani and connecting the region to larger trade and administrative centres.
The railway network later expanded with the addition of the Parbhani–Parli Vaijnath line, which branches off to connect Parbhani with Parli Vaijnath (Beed district, Maharashtra), passing through predominantly agricultural zones. Another significant line is the Khandwa–Akola–Purna line, which connects through Purna Junction, linking parts of Maharashtra with Khandwa in Madhya Pradesh.
Notably, historical records such as the district Gazetteer (1967) indicate that the planning and construction of these lines responded to the region’s growing need for reliable transport of agricultural produce, particularly cotton and other cash crops, to wider markets. Today, the railway network remains a key component of Parbhani district’s transport infrastructure, providing connectivity to major cities in Maharashtra and neighbouring states.
Overview of Bus Networks
Parbhani district is currently served by a combination of public and private bus services that provide passenger transport within the district and to neighbouring regions. The Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation (MSRTC) operates regular state-run bus services connecting major towns, villages, and district centres. Alongside MSRTC operations, privately operated buses and smaller transport operators also run services on local and inter-district routes
Notably, organised bus transport in Parbhani began in 1932 when the Nizam State Government nationalised local transport services, introducing scheduled passenger routes under public management. The establishment of a bus depot at Jintur in 1955 supported more reliable services by connecting settlements through metalled roads and improving access across the district. In 1961, the Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation was formed to manage state-run bus services in Maharashtra. Today, bus services remain important for the population of the district.
Ferries & Water Transport
Parbhani district is situated within the Godavari river basin and is crossed by rivers such as the Godavari, Purna, Dudhana, Karpara, Khaid, and Penganga, along with their tributaries. Historically, these waterways provided local routes for the movement of people and goods, especially before the expansion of road infrastructure. Such services were regulated by local authorities to maintain safety and regularity of operations.
In areas where road access was limited, it is mentioned in the district Gazetteer (1967) that ferry services were used to cross rivers and reach nearby settlements. Several ferry ghats operated in talukas such as Gangakhed, Basmat, and Pimpligoan, where they served villages located near major rivers. While later road and bridge construction reduced dependence on ferries, these crossings historically provided important connectivity for the population of the district.
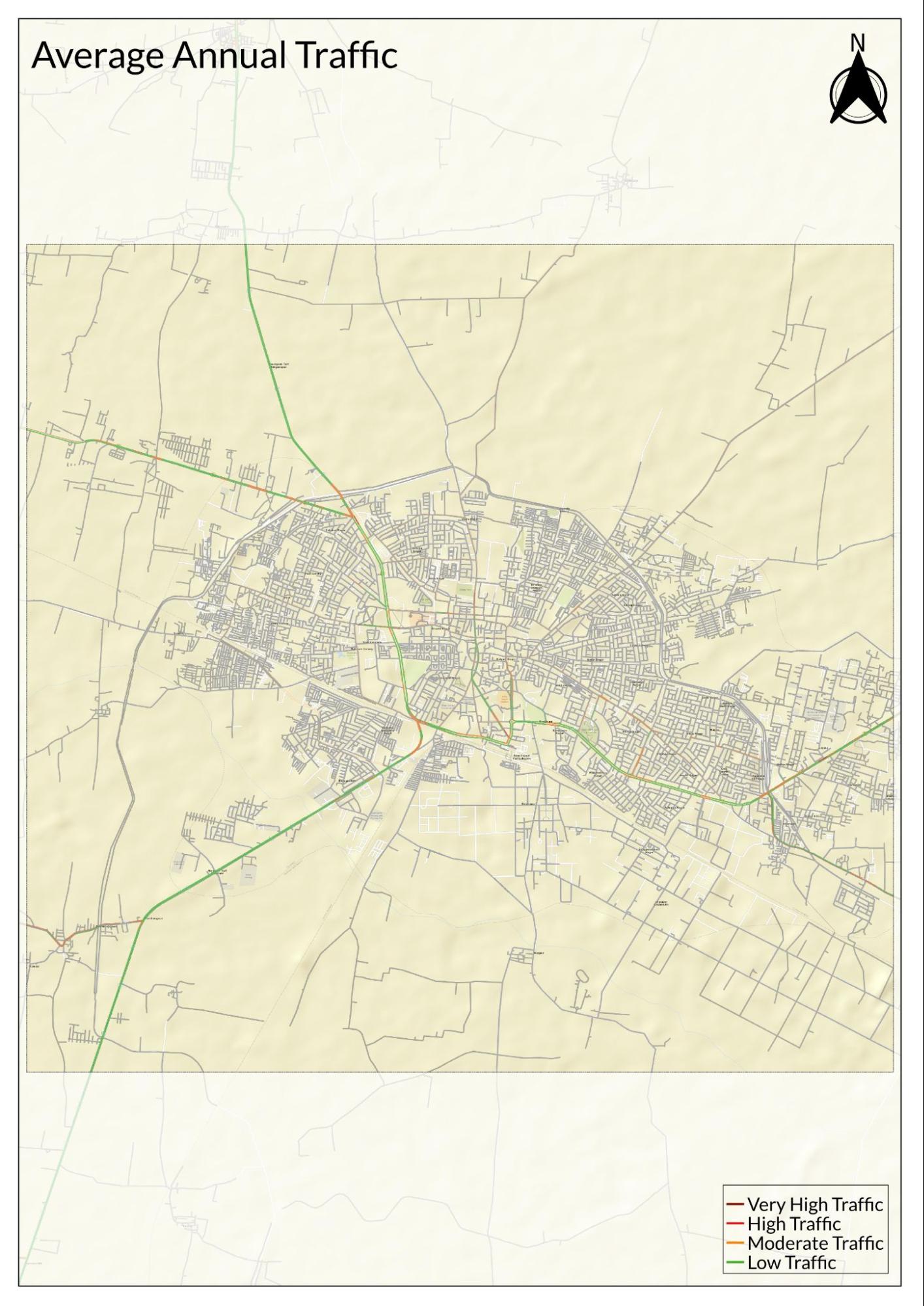
Traffic Map
Communication Networks
Newspapers & Magazines
During the early 1960s, according to the district Gazetteer (1967), there were three Marathi daily newspapers and one Hindi daily circulating in the district. In addition to these dailies, the district had three Marathi weeklies — Jagriti, Tarun Maharashtra, and Lokmanya — and one Hindi weekly, Parbhani Samachar.
These publications covered local matters, culture, and the socio-political context of the district. In later years, the number of newspapers and magazines in Parbhani increased as literacy rates and demand for printed information grew.
Graphs
Road Safety and Violations
Transport Infrastructure
Bus Transport
Communication and Media
Sources
Bina Sengar. 2016. Trade Routes and Commercial Networks in Deccan-Marathwada During the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Century. In Salma Farooqui (eds.).Histories, Regions, Nodes. Primus Books.
Maharashtra State Gazetteers. 1967.Parbhani District.Directorate of Government Printing, Stationary & Publications, Government of Maharashtra, Mumbai.
Parbhani District Information. Rail Yatri.https://www.railyatri.in/districts/parbhani#…
World Health Organization.Road Safety.WHO, Geneva.https://www.who.int/health-topics/road-safet…
Last updated on 6 November 2025. Help us improve the information on this page by clicking on suggest edits or writing to us.